Elements named after continents are chemical elements whose names are derived from the names of continents. These elements were discovered and named by scientists who wanted to honor the continents where they were found.
There are four elements that have been named after continents. The first of these was europium, which was named after the continent of Europe. Europium was discovered in 1896 by the French chemist Eugne-Anatole Demaray. The other three elements that have been named after continents are americium, which was named after the Americas; asium, which was named after Asia; and australium, which was named after Australia.
The discovery of these elements has helped scientists to better understand the composition of the Earth's crust. These elements are also used in a variety of applications, including electronics, medicine, and energy production.
Elements named after continents
Elements named after continents are a unique group of chemical elements that have been discovered and named in honor of the continents where they were first found. These elements play a vital role in various scientific and technological applications, and their discovery has significantly contributed to our understanding of the Earth's composition.
- Historical Significance: The naming of elements after continents reflects the historical and geographical context of their discovery, providing insights into the exploration and scientific advancements of different eras.
- Geographical Diversity: These elements represent the diverse geological and mineral resources found across different continents, highlighting the unique characteristics of each region.
- Scientific Importance: The discovery and study of elements named after continents have deepened our understanding of the periodic table and the properties of elements, contributing to the advancement of chemistry and materials science.
- Technological Applications: Many elements named after continents are used in various technological applications, including electronics, medicine, and energy production, demonstrating their practical significance.
- Cultural and Educational Value: These elements serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness between science, geography, and culture, fostering an appreciation for the diversity and wonders of our planet.
- Exploration and Discovery: The discovery of elements named after continents showcases the spirit of exploration and the pursuit of scientific knowledge, inspiring future generations of scientists and researchers.
- Global Collaboration: The naming of elements after continents often involves international collaboration and recognition, highlighting the global nature of scientific research and discovery.
- Interdisciplinary Connections: These elements provide a bridge between different scientific disciplines, such as geology, chemistry, and history, fostering interdisciplinary research and a holistic understanding of the world.
- Sustainability and Resource Management: The study of elements named after continents contributes to sustainable resource management and conservation efforts, as it provides insights into the distribution and availability of these elements.
In conclusion, elements named after continents are not only fascinating from a scientific perspective but also hold cultural, historical, and educational significance. Their discovery and study have played a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the Earth, advancing technology, and inspiring future generations of explorers and scientists.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of naming elements after continents lies in the fact that it provides valuable insights into the exploration and scientific advancements of different eras. By examining the historical context surrounding the discovery of these elements, we can gain a deeper understanding of the scientific motivations, technological capabilities, and geographical factors that influenced their identification and characterization.
For instance, the discovery of europium in 1896 by the French chemist Eugne-Anatole Demaray marked a significant milestone in the exploration of the rare earth elements. The naming of europium after the continent of Europe reflects the scientific community's recognition of the importance of geographical location in the discovery and study of new elements.
Similarly, the naming of americium, asium, and australium after the continents of America, Asia, and Australia, respectively, highlights the global nature of scientific exploration and the desire to honor the contributions of different regions to the advancement of knowledge.
Understanding the historical significance of naming elements after continents allows us to appreciate the complex interplay between scientific discovery, geographical exploration, and cultural influences. It also underscores the importance of recognizing and celebrating the contributions of scientists from diverse backgrounds to our collective understanding of the world.
Geographical Diversity
The connection between geographical diversity and elements named after continents is significant in several ways. Firstly, the naming of elements after continents reflects the unique geological and mineral resources found in each region. For instance, europium was discovered in Europe, which is known for its rich deposits of rare earth minerals. Similarly, americium was discovered in the Americas, which is home to a variety of mineral resources, including uranium and thorium.
- Geological Diversity: The geological diversity of continents is reflected in the variety of elements found there. For example, europium is associated with granite pegmatites, which are igneous rocks formed from the cooling of molten rock. In contrast, americium is found in uranium ores, which are sedimentary rocks formed from the accumulation and consolidation of uranium-bearing materials.
- Mineral Resources: The mineral resources of continents play a crucial role in the discovery and production of elements named after them. For instance, the abundance of rare earth minerals in Europe facilitated the discovery and extraction of europium. Similarly, the availability of uranium ores in the Americas enabled the production of americium.
- Unique Characteristics: Each continent possesses unique geological and mineral characteristics that contribute to the discovery of new elements. These unique characteristics, such as specific rock formations, mineral deposits, and geological processes, provide valuable insights into the Earth's geological history and the distribution of elements.
- Scientific Exploration: The geographical diversity of continents drives scientific exploration and the search for new elements. Geologists and mineralogists are drawn to regions with unique geological features and mineral resources, increasing the likelihood of discovering new elements and expanding our understanding of the periodic table.
In conclusion, the geographical diversity of continents is closely linked to the discovery and naming of elements. The unique geological and mineral resources found in different regions have played a significant role in enriching our knowledge of the elements and their distribution on Earth.
Scientific Importance
The connection between scientific importance and elements named after continents lies in the fact that the discovery and study of these elements have significantly contributed to our understanding of the periodic table and the properties of elements. This, in turn, has led to advancements in chemistry and materials science.
- Periodic Table: The discovery of elements named after continents has helped to complete the periodic table and refine our understanding of the chemical properties of elements. For example, the discovery of europium filled a gap in the periodic table and provided insights into the behavior of rare earth elements.
- Element Properties: The study of elements named after continents has deepened our understanding of the properties of elements and their behavior in different chemical reactions. For instance, the study of americium has contributed to our knowledge of radioactive elements and their potential applications in nuclear energy.
- Chemical Bonding: The discovery and study of elements named after continents have also shed light on chemical bonding and the interactions between elements. For example, the study of asium has provided insights into the bonding behavior of heavy elements and their potential use in new materials.
- Materials Science: The knowledge gained from studying elements named after continents has led to the development of new materials with unique properties. For instance, the discovery of australium has contributed to the development of high-strength alloys and wear-resistant materials.
In conclusion, the scientific importance of elements named after continents lies in their role in advancing our understanding of the periodic table, element properties, chemical bonding, and materials science. The discovery and study of these elements have not only expanded our knowledge of chemistry but also paved the way for the development of new technologies and materials.
Technological Applications
The practical significance of elements named after continents stems from their wide range of applications in various technological fields. These elements possess unique properties that make them indispensable for modern technologies, contributing to advancements in electronics, medicine, and energy production.
- Electronics: Europium is a vital component in red phosphors used in color television screens and fluorescent lighting. Americium is employed in smoke detectors, ionization chambers, and neutron sources. Asium has potential applications in semiconductor technology and high-temperature superconductors.
- Medicine: Americium-241 is used in medical imaging techniques such as bone scans. Europium complexes are employed as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Asium exhibits promise in the development of targeted cancer therapies and diagnostic imaging agents.
- Energy Production: Americium is utilized in nuclear reactors as a source of neutrons. Asium is being investigated for its potential role in nuclear fusion reactions. Australium has applications in the production of wear-resistant materials for nuclear power plants.
In conclusion, the technological applications of elements named after continents underscore their practical value. These elements play critical roles in electronic devices, medical diagnostics and treatments, and energy production. Their unique properties and versatility make them essential components in advancing various technologies that benefit society.
Cultural and Educational Value
The cultural and educational value of elements named after continents lies in their ability to connect science, geography, and culture, fostering an appreciation for the diversity and wonders of our planet. These elements serve as tangible reminders of the interconnectedness of human knowledge and the natural world.
By understanding the origins and significance of elements named after continents, we gain insights into the history of scientific exploration, the diversity of geological formations, and the cultural significance of different regions. For example, the naming of europium after Europe highlights the historical importance of the continent in scientific research and discovery.
Furthermore, studying elements named after continents can inspire future generations of scientists and explorers. By learning about the unique properties and applications of these elements, students can develop an appreciation for the wonders of the natural world and the potential for scientific discovery.
In conclusion, the cultural and educational value of elements named after continents is significant. These elements provide a bridge between science, geography, and culture, fostering an appreciation for the diversity and wonders of our planet. Understanding their origins and significance can inspire future generations of scientists and explorers.
Exploration and Discovery
The discovery of elements named after continents is closely intertwined with the spirit of exploration and the pursuit of scientific knowledge. Throughout history, scientists have embarked on expeditions to unexplored regions, driven by a desire to understand the natural world and its composition. The discovery of new elements, including those named after continents, has been a testament to the human spirit of adventure and the quest for knowledge.
The naming of elements after continents serves as a recognition of the geographical and geological diversity of our planet. It highlights the unique characteristics of each continent and the contributions of scientists from different regions to the advancement of chemistry and science as a whole. These discoveries have not only expanded our understanding of the periodic table but have also inspired future generations of scientists and researchers.
For instance, the discovery of europium, named after the continent of Europe, in the late 19th century sparked interest in the study of rare earth elements. Similarly, the discovery of americium, named after the Americas, in the mid-20th century played a significant role in the development of nuclear science and technology. These discoveries, among others, have fueled the pursuit of scientific knowledge and continue to inspire young minds to explore the unknown.
In conclusion, the exploration and discovery of elements named after continents are integral to the advancement of scientific knowledge and the human spirit of exploration. They serve as a reminder of the interconnectedness of science, geography, and culture, and inspire future generations to push the boundaries of human understanding.
Global Collaboration
The naming of elements after continents underscores the collaborative nature of scientific research and discovery. It necessitates international cooperation, shared knowledge, and the recognition of scientific contributions across borders.
- Shared Knowledge and Expertise: Scientific research often requires the expertise and collaboration of scientists from diverse backgrounds and institutions. The naming of elements after continents reflects the collective knowledge and efforts of scientists worldwide.
- International Recognition: The decision to name an element after a continent is a testament to the global recognition and significance of scientific discoveries. It acknowledges the contributions of scientists from specific regions and fosters a sense of international scientific community.
- Cultural Exchange: The naming of elements after continents promotes cultural exchange and understanding. It connects scientific discoveries to geographical and cultural contexts, fostering appreciation for the diversity of scientific perspectives.
- Inspiration for Future Collaboration: The recognition of international collaboration in naming elements inspires future scientists to engage in global partnerships and research endeavors.
In conclusion, the global collaboration involved in naming elements after continents highlights the interconnectedness of scientific research and the importance of international cooperation in advancing our understanding of the world.
Interdisciplinary Connections
The connection between "Interdisciplinary Connections: These elements provide a bridge between different scientific disciplines, such as geology, chemistry, and history, fostering interdisciplinary research and a holistic understanding of the world." and "elements named after a continent" is significant, as these elements serve as tangible examples of how scientific disciplines intersect and complement each other. By studying elements named after continents, scientists can gain insights into the geological processes that formed these elements, the chemical properties that make them unique, and the historical context surrounding their discovery and naming.
For instance, the study of europium, named after the continent of Europe, requires an interdisciplinary approach that combines geology to understand the geological formations in which it is found, chemistry to analyze its atomic structure and properties, and history to trace the scientific journey that led to its discovery and naming. This interdisciplinary approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of europium than any single discipline could offer on its own.
Furthermore, the discovery and study of elements named after continents have practical significance. They have led to advancements in various fields, including electronics, medicine, and energy production. For example, americium, named after the Americas, is used in smoke detectors and medical imaging techniques. By understanding the interdisciplinary connections between geology, chemistry, and history, scientists can continue to explore and harness the potential of elements named after continents for the benefit of society.
In conclusion, the interdisciplinary connections fostered by elements named after a continent provide a valuable framework for scientific research and a deeper understanding of the world around us. They encourage collaboration between different scientific disciplines, leading to a more comprehensive and holistic approach to scientific discovery and innovation.
Sustainability and Resource Management
Understanding the distribution and availability of elements named after continents is crucial for sustainable resource management and conservation. By studying the geological formations and processes that concentrate these elements, scientists can develop strategies to extract and utilize them responsibly while minimizing environmental impact.
- Geological Context: Studying the geological context of elements named after continents provides insights into their formation and distribution. This knowledge helps in identifying potential reserves and developing targeted exploration strategies.
- Environmental Impact: Mining and processing elements named after continents can have environmental consequences. Understanding the environmental impact of these activities allows for the development of sustainable practices that minimize ecological damage.
- Resource Conservation: By understanding the distribution and availability of elements named after continents, scientists can develop strategies to conserve these resources and prevent overexploitation.
- Recycling and Recovery: Studying the properties and behavior of elements named after continents can lead to the development of innovative recycling and recovery techniques, reducing waste and conserving resources.
In conclusion, the study of elements named after continents plays a vital role in sustainable resource management and conservation. By understanding the geological context, environmental impact, and resource conservation strategies, scientists and policymakers can ensure the responsible and sustainable use of these valuable elements for present and future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Elements Named After Continents
This section addresses some common questions and misconceptions surrounding elements named after continents, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: How many elements are named after continents?
There are four elements named after continents: europium (Europe), americium (Americas), asium (Asia), and australium (Australia).
Question 2: Who discovered these elements and when?
Europium was discovered by the French chemist Eugne-Anatole Demaray in 1896. Americium was discovered by a team of American scientists led by Glenn T. Seaborg in 1944. Asium and australium were discovered by a team of Australian scientists led by Mark Oliphant in 1948.
Question 3: What are some of the unique properties of these elements?
Europium is a soft, silvery-white metal that is highly reactive. Americium is a radioactive element that emits alpha particles. Asium is a synthetic element that is extremely rare and has not been found naturally. Australium is a hypothetical element that has not yet been confirmed to exist.
Question 4: What are the practical applications of these elements?
Europium is used in phosphors for lighting and television screens. Americium is used in smoke detectors and neutron sources. Asium has potential applications in nuclear medicine and cancer treatment. Australium, if it exists, could have potential applications in high-temperature superconductors.
Question 5: Why are these elements named after continents?
The elements were named after continents to honor the regions where they were discovered or to reflect their geographical origins. For example, europium was named after Europe because it was first found in minerals from that continent.
Question 6: Are there any other elements named after geographical locations?
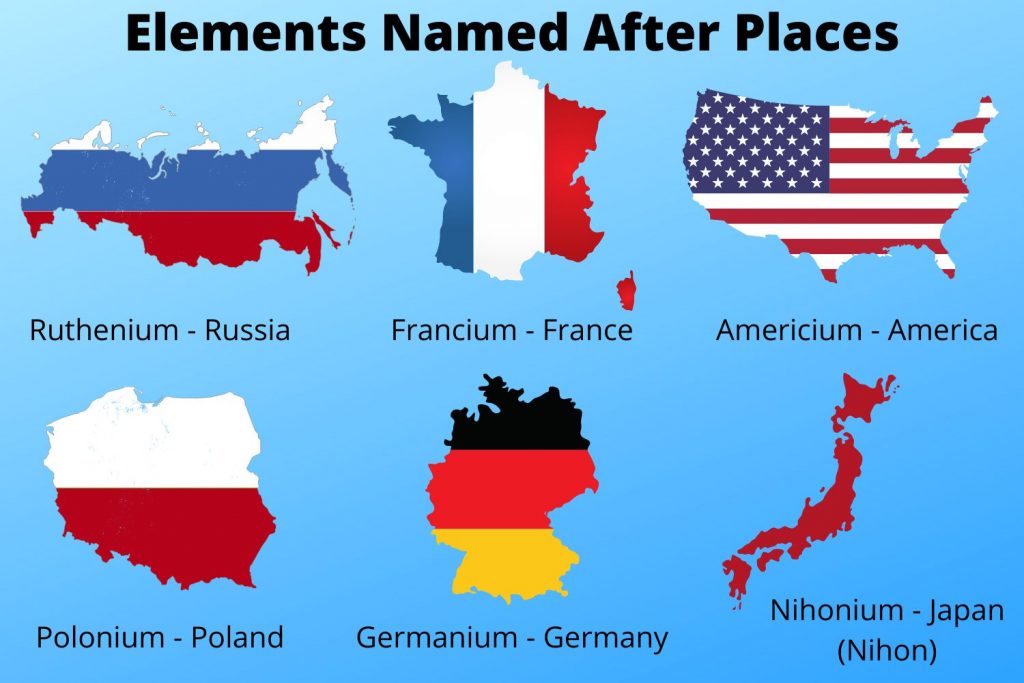
Yes, there are a few other elements named after geographical locations, such as francium (France), polonium (Poland), and rutherfordium (after the physicist Ernest Rutherford, who was born in New Zealand).
In conclusion, elements named after continents offer insights into the history of scientific discovery, the diversity of geological formations, and the practical applications of rare and unique elements.
Tips on Exploring Elements Named After Continents
Delving into the topic of elements named after continents offers a fascinating journey through scientific discovery, geography, and the diversity of our planet. Here are a few tips to enhance your exploration of this subject:
Seek Historical Context: Understanding the historical context surrounding the discovery of these elements provides valuable insights into the scientific advancements and geographical expeditions of different eras. Explore the lives of the scientists involved and the challenges they faced in identifying and characterizing these elements.
Examine Geographical Distribution: The geographical distribution of elements named after continents reflects the unique geological formations and mineral resources found in each region. Study the geological maps and learn about the specific rock types and geological processes that concentrate these elements in certain areas.
Analyze Chemical Properties: Delve into the chemical properties of elements named after continents to understand their behavior in different chemical reactions. Examine their reactivity, oxidation states, and interactions with other elements. This knowledge will enhance your comprehension of their potential applications and limitations.
Explore Technological Applications: Many elements named after continents have found practical applications in various technological fields. Investigate how these elements are used in electronics, medicine, energy production, and other industries. Understanding their technological significance will highlight their impact on modern society.
Consider Global Collaboration: The naming of elements after continents often involves international collaboration and recognition. Learn about the scientific partnerships and exchanges that have contributed to the discovery and study of these elements. This will emphasize the global nature of scientific research and innovation.
By following these tips, you will gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of elements named after continents. Their discovery, properties, and applications offer a compelling narrative that connects science, geography, and human endeavor.
In conclusion, exploring elements named after continents is not only an educational pursuit but also a journey of scientific discovery, cultural appreciation, and global interconnectedness.
Conclusion
Our exploration of elements named after continents has traversed the realms of scientific discovery, geographical diversity, and technological applications. These elements serve as tangible reminders of the interconnectedness between science, geography, and human culture.
Their discovery and study have expanded our understanding of the periodic table, the properties of elements, and the geological processes that shape our planet. The unique characteristics of each continent are reflected in the elements that bear their names, highlighting the diversity and wonder of the natural world.
As we continue to explore the vast expanse of scientific knowledge, the study of elements named after continents will undoubtedly yield further insights and applications. They stand as a testament to the human spirit of exploration, the pursuit of knowledge, and the enduring power of scientific collaboration.
Unveiling The Truth: Ant McPartlin's Exciting Pregnancy Journey
Unveiling The Magic: Alastair Wallace Stewart's Odyssey As Rod Stewart
Unveiling The Wealth Of Boris Epshteyn: A Net Worth Discovery
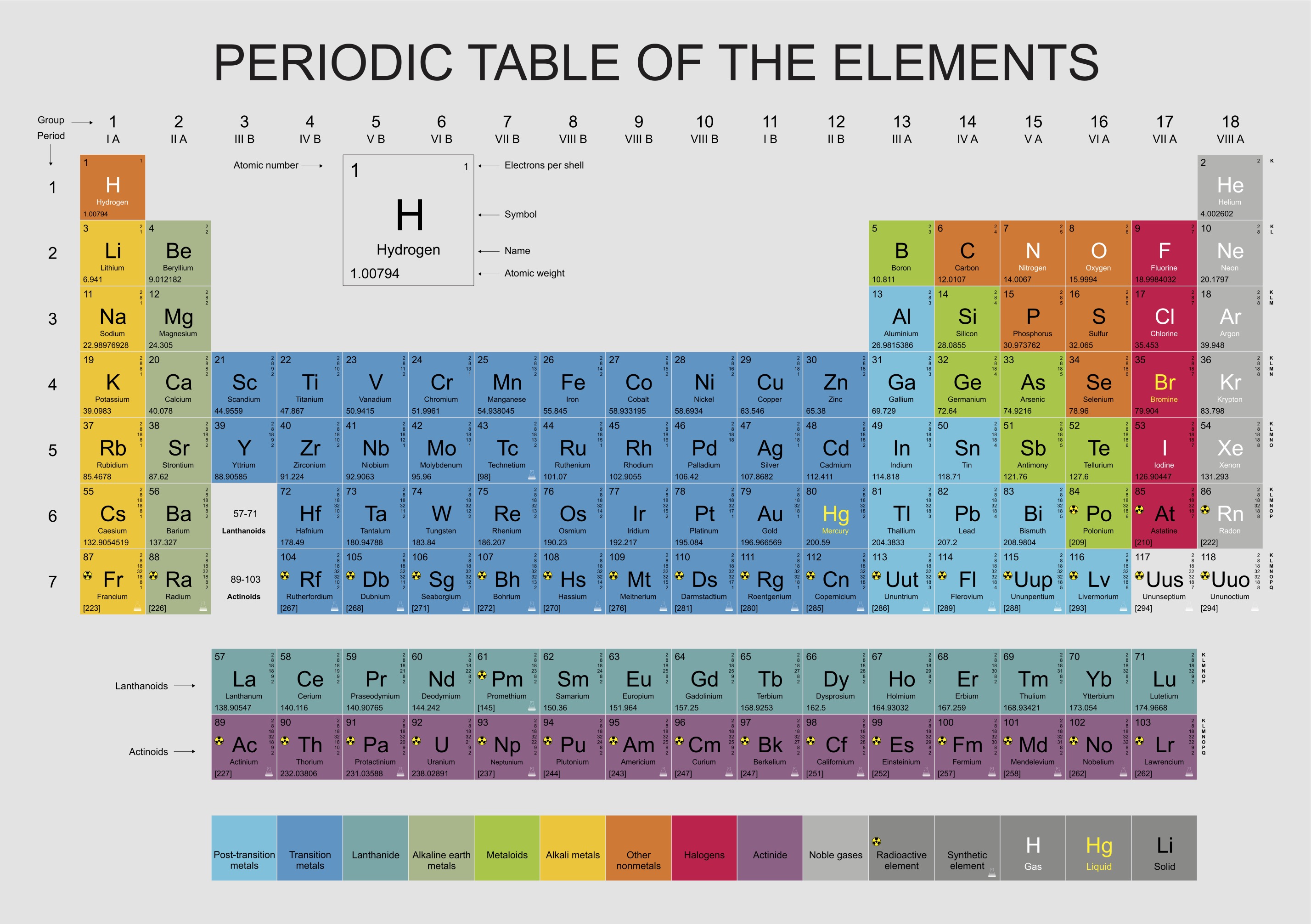
periodic table of elements printable flashcards chemistry periodic
5 Elements Named in Honor of Notable Scientists Discover Magazine
ncG1vNJzZmisqauvpr6RZ6psZqWoerix0q1ka2aRoq67u82arqxmk6S6cLHLnqSepqSoeq%2BtzJ6bZpmWqbKzecBmmqimpJ67prrTZ5%2BtpZw%3D